Java Basics Practice
Variable that are declared inside method - local
Variable that are declared inside class and outside method - instance
Variable that are declared as static - static, Static can't be local
-------------------------------------------------
data type types: primitive: int, long, float, short, double, boolean, char, byte
non-primitive: Array, String
-------------------------------------------------
Object: It is an entity that has state, behavior and identity. eg: chair- solid, tall, brown - state. Behavior - for sitting. Identity - table from my home which is unique. It can be physical or logical.
Class: Collection of object, only logical
When object acquires properties of parent object - inheritance. Eg. dog can acquire properties of Animal. Dog itself can bark and can eat like other animals.
To perform one task in different ways - polymorphism. Eg. Draw() - it can be drawCircle() or drawRectangle() or other. Eg. Speak() - cat can meow, dog can bark.
Hiding internal details and showing only functionality - abstraction. Eg- Email or SMS.
Binding code and data into single unit - encapsulation.
------------------------------------------------------
OOPs advantage - develop and maintenance easy, data hiding, simulate real world.
---------------------------------------------------
Constructor is a special type of method to initialize the object. Invoked implicitly at the time of object creation. Name - same as class and no Return type. Default (no argument- provides default value to the object.) and parameterized (with argument - provide different value to the different object) constructor.
---------------------------------------------------------
- Note: Multiple inheritance is not supported in java through class but can be achieved using interface.
---------------------------------------------------------
If a class has multiple method with same name but different parameters - method overloading (to increase readability). (WITHIN CLASS) (Compile time polymorphism). Can be achieved by using different number of arguments or data types.
In java, Method Overloading is not possible by changing the return type of the method only because of ambiguity.
-------------------------------------------
Variable that are declared inside class and outside method - instance
Variable that are declared as static - static, Static can't be local
-------------------------------------------------
data type types: primitive: int, long, float, short, double, boolean, char, byte
non-primitive: Array, String
-------------------------------------------------
Object: It is an entity that has state, behavior and identity. eg: chair- solid, tall, brown - state. Behavior - for sitting. Identity - table from my home which is unique. It can be physical or logical.
Class: Collection of object, only logical
When object acquires properties of parent object - inheritance. Eg. dog can acquire properties of Animal. Dog itself can bark and can eat like other animals.
To perform one task in different ways - polymorphism. Eg. Draw() - it can be drawCircle() or drawRectangle() or other. Eg. Speak() - cat can meow, dog can bark.
Hiding internal details and showing only functionality - abstraction. Eg- Email or SMS.
Binding code and data into single unit - encapsulation.
------------------------------------------------------
OOPs advantage - develop and maintenance easy, data hiding, simulate real world.
---------------------------------------------------
Constructor is a special type of method to initialize the object. Invoked implicitly at the time of object creation. Name - same as class and no Return type. Default (no argument- provides default value to the object.) and parameterized (with argument - provide different value to the different object) constructor.
---------------------------------------------------------
Q) Does constructor return any value?
Ans:yes, that is current class instance (You cannot use return type yet it returns a value.
This is an implicit event. If you do not create constructor, the program will create default
constructor internally.).
This is an implicit event. If you do not create constructor, the program will create default
constructor internally.).
Can constructor perform other tasks instead of initialization?
Yes, like object creation, starting a thread, calling method etc. You can perform any operation
in the constructor as you perform in the method.
------------------------------------------------------------
Static keyword is used for memory management. It is related to class rather than object. Method and variable can be static (class variable, class method). Static variable is used to refer common property. Eg name of School of all the students. Static variable gets memory only once at the time of class loading - memory efficient. Static method can be invoked without creating object and can access static data member.
Java static property is shared to all objects.
------------------------------------------------------------
Static keyword is used for memory management. It is related to class rather than object. Method and variable can be static (class variable, class method). Static variable is used to refer common property. Eg name of School of all the students. Static variable gets memory only once at the time of class loading - memory efficient. Static method can be invoked without creating object and can access static data member.
Java static property is shared to all objects.
Q) why java main method is static?
Ans) because object is not required to call static method if it were non-static method, jvm
create object first then call main() method that will lead the problem of extra memory
allocation.
Q) Can we execute a program without main() method?
No from JDK 1.7
Before it was possible using Static block.
-----------------------------------------
"this" keyword is used to refer current class object.
It is better approach to use meaningful names for variables. So we use same name for instance
variables and parameters in real time, and always use this keyword.
--------------------------------------------------------
-Inheritance is used for method overriding - so run-time polymorphism is achieved. If sub-class has same method name as the parent class it is called method overriding. (BETWEEN TWO CLASSES) Methods must have same parameter as parent class method. - Note: Multiple inheritance is not supported in java through class but can be achieved using interface.
---------------------------------------------------------
If a class has multiple method with same name but different parameters - method overloading (to increase readability). (WITHIN CLASS) (Compile time polymorphism). Can be achieved by using different number of arguments or data types.
In java, Method Overloading is not possible by changing the return type of the method only because of ambiguity.
-------------------------------------------
Can we override static method?
No, static method cannot be overridden.
Why we cannot override static method?
because static method is bound with class whereas instance method is bound with object.
Static belongs to class area and instance belongs to heap area.
Can we override java main method?
No, because main is a static method.
-----------------------------------------------
"super" keyword is used to refer immediate parent class object. When you create an instance of child class, an instance of parent class is implicitly created and is referred by super keyword. It can invoke immediate parent class constructors and methods.
--------------------------------------------------
"final" keyword is used for method (can be extended but can't be overridden ), variable (constant) and class (can't be extended). It is used to restrict user.
Q) Is final method inherited?
Ans) Yes, final method is inherited but you cannot override it.
In java we cannot override a final method but is it possible to overload ?
Yes, overloading a final method is perfectly legitimate.
For example:
public final void doStuff(int x) { ... }
public final void doStuff(double x) { ... }Q) What is blank or uninitialized final variable?
A final variable that is not initialized at the time of declaration is known as blank final variable.
If you want to create a variable that is initialized at the time of creating object and once
initialized may not be changed, it is useful. It can be initialized only in constructor.
A final variable that is not initialized at the time of declaration is known as blank final variable.
If you want to create a variable that is initialized at the time of creating object and once
initialized may not be changed, it is useful. It can be initialized only in constructor.
initialized may not be changed, it is useful. It can be initialized only in constructor.
Q) Can we declare a constructor final?
No, because constructor is never inherited.
No, because constructor is never inherited.
Why can't constructors be final, static, or abstract in Java?
1. When you set a method as final it means: "You don't want any class override it." But the constructor (according to the Java Language Specification) can't be overridden, so it is clean.
2. When you set a method as abstract it means: "The method doesn't have a body and it should be implemented in a child class." But the constructor is called implicitly when the new keyword is used so it can't lack a body.
3. When you set a method as static it means: "The method belongs to the class, not a particular object." But the constructor is implicitly called to initialize an object, so there is no purpose in having a static constructor.
1. Constructors aren't inherited so can't be overridden so whats the use to have final constructor
2. Constructor is called automatically when an instance of the class is created, it has access to instance fields of the class. What will be the use of a static constructor.
3. Constructor can't be overridden so what will you do with an abstract constructor.
--------------------------------------------------
instanceof operator is used to check whether the object is instance of a class/interface. It returns either true or false.
--------------------------------------------------
a class that is declared with abstract keyword is called abstract class- process of hiding details. Can't be instantiated (because some part of it is not defined)
abstract class - (0-100)% abstraction. Interface- 100% abstraction
abstract method does not have body.
An abstract class can have data member, abstract method and constructor.
If there is any abstract method in a class, that class must be abstract.
If you are extending any abstract class that have abstract method, you must either provide the implementation of the method or make this class abstract.
-------------------------------------------------------------
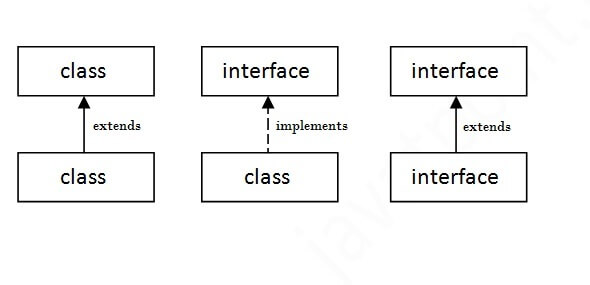
Interface is a blueprint of a class. It can have static constants and abstract methods. Interface- to achieve abstraction. Can't be instantiated. Help to achieve multiple inheritance.
The java compiler adds public and abstract keywords before the interface method. More, it adds public, static and final keywords before data members. In other words, Interface fields are public, static and final by default, and methods are public and abstract.
final it means: "You don't want any class override it." But the constructor (according to the Java Language Specification) can't be overridden, so it is clean.abstract it means: "The method doesn't have a body and it should be implemented in a child class." But the constructor is called implicitly when the new keyword is used so it can't lack a body.static it means: "The method belongs to the class, not a particular object." But the constructor is implicitly called to initialize an object, so there is no purpose in having a static constructor.

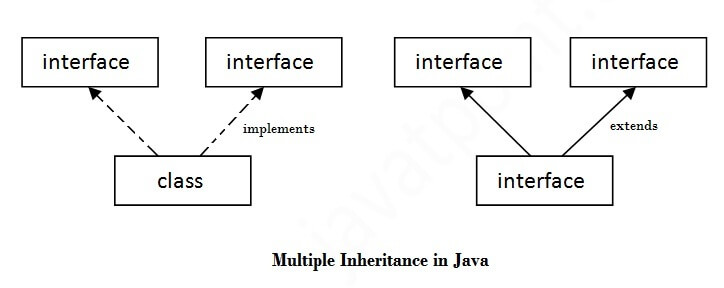
Q) Multiple inheritance is not supported through class in java but it
is possible by interface, why?
As we have explained in the inheritance chapter, multiple inheritance is not supported in case
of class because of ambiguity. But it is supported in case of interface because there
is no ambiguity as implementation is provided by the implementation class.
1) Abstract class can have abstract and non-abstract methods. Interface can have only abstract methods. Since Java 8, it can have default and static methods also.
2) Abstract class doesn't support multiple inheritance. Interface supports multiple inheritance.
3) Abstract class can have final, non-final, static and non-static variables. Interface has only static and final variables.
4) Abstract class can provide the implementation of interface. Interface can't provide the implementation of abstract class.
-------------------------------------------------
Encapsulation: process of wrapping code and data together. If the data member is made private, we can use setter and getter method to make the class write only or read only.
Comments
Post a Comment