Java 2018 - Basic Theory
JAVA
Java is a programming Language and a platform.
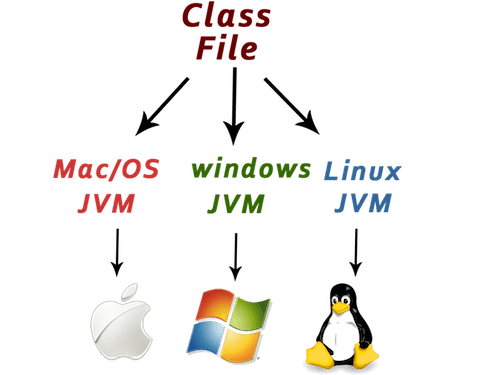
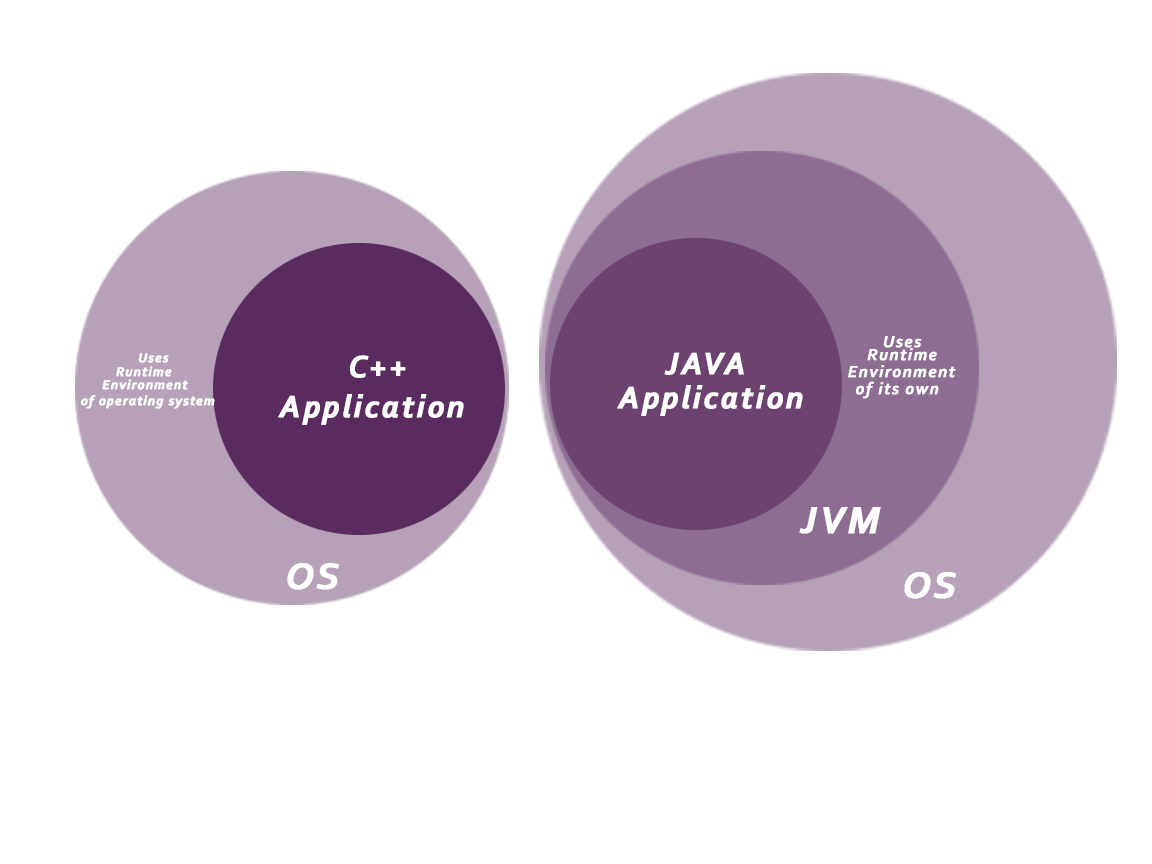
Platform: Any environment in which a program runs is called a platform. Since Java has its own JRE and API, it is also a platform.
The latest version is Java 9, released on September 21, 2017.
Java is a programming Language and a platform.
Platform: Any environment in which a program runs is called a platform. Since Java has its own JRE and API, it is also a platform.
The latest version is Java 9, released on September 21, 2017.
Versions
Major release versions of Java, along with their release dates:
- JDK 1.0 (January 23, 1996)
- JDK 1.1 (February 19, 1997)
- J2SE 1.2 (December 8, 1998)
- J2SE 1.3 (May 8, 2000)
- J2SE 1.4 (February 6, 2002)
- J2SE 5.0 (September 30, 2004)
- Java SE 6 (December 11, 2006)
- Java SE 7 (July 28, 2011)
- Java SE 8 (March 18, 2014)
- Java SE 9 (September 21, 2017)
Oracle Corporation is the current owner of the official implementation of the Java SE platform, following their acquisition of Sun Microsystems on January 27, 2010. This implementation is based on the original implementation of Java by Sun.
Java is used in Desktop application, web application, Mobile application, embedded system, robotics, games, enterprise application, etc.
There are many 4 types of application that can be created using Java:
1)Standalone, 2)Web, 3)Enterprise, 4)Mobile
There are 4 Java platforms/editions:
1) Java SE, 2) Java EE, 3) Java ME, 4)JavaFx
Java SE includes Java programming APIs such as java.lang, java.io, java.net, java.util, java.sql, java.math etc. It includes core topics like OOPs, String, Regex, Exception, Inner classes, Multithreading, I/O Stream, Networking, AWT, Swing, Reflection, Collection etc.
Java EE is an enterprise platform which is mainly used to develop web and enterprise applications. It is built on the top of Java SE platform. It includes topics like Servlet, JSP, Web Services, EJB, JPA etc.
Java ME is used for mobile application and JavaFx is used for light-weight user interface API.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
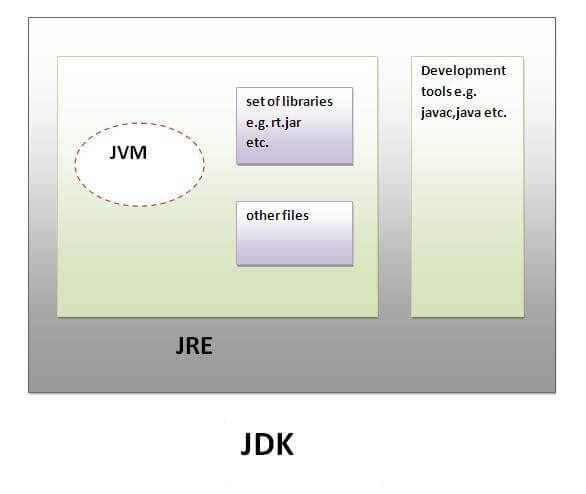
Difference between JDK, JRE and JVM:
JVM (Java Virtual Machine) is an abstract machine. It is a specification that provides runtime environment in which java bytecode can be executed.
JVMs are available for many hardware and software platforms. JVM, JRE and JDK are platform dependent because configuration of each OS differs. But, Java is platform independent.
The JVM performs following main tasks:
- Loads code
- Verifies code
- Executes code
- Provides runtime environment
JRE is an acronym for Java Runtime Environment.It is used to provide runtime environment.It is the implementation of JVM. It physically exists. It contains set of libraries + other files that JVM uses at runtime. Implementation of JVMs are also actively released by other companies besides Sun Micro Systems.
JDK is an acronym for Java Development Kit.It physically exists.It contains JRE + development tools.

java -version // this will check your jre version
javac -version // this will check your java compiler version if you installed
The JDK has as its primary components a collection of programming tools, including:
- appletviewer – this tool can be used to run and debug Java applets without a web browser
- apt – the annotation-processing tool
- extcheck – a utility that detects JAR file conflicts
- java – the loader for Java applications. This tool is an interpreter and can interpret the class files generated by the javac compiler. Now a single launcher is used for both development and deployment. The old deployment launcher, jre, no longer comes with Sun JDK, and instead it has been replaced by this new java loader.
- javac – the Java compiler, which converts source code into Java bytecode
- javadoc – the documentation generator, which automatically generates documentation from source code comments
- jar – the archiver, which packages related class libraries into a single JAR file. This tool also helps manage JAR files.
- JConsole – Java Monitoring and Management Console
- jdb – the debugger
- jrunscript – Java command-line script shell..
- VisualVM – visual tool integrating several command-line JDK tools and lightweight performance and memory profiling capabilities
- xjc – Part of the Java API for XML Binding (JAXB) API. It accepts an XML schema and generates Java classes.
- As well as many more check wikipedia.
Experimental tools may not be available in future versions of the JDK.
The JDK also comes with a complete Java Runtime Environment, usually called a private runtime, due
to the fact that it is separated from the "regular" JRE and has extra contents. It consists of a Java Virtual Machine and all of the class libraries present in the production environment, as well as additional libraries only useful to developers, such as the internationalization libraries and the IDL libraries.
to the fact that it is separated from the "regular" JRE and has extra contents. It consists of a Java Virtual Machine and all of the class libraries present in the production environment, as well as additional libraries only useful to developers, such as the internationalization libraries and the IDL libraries.
Copies of the JDK also include a wide selection of example programs demonstrating the use of almost all portions of the Java API.
Ambiguity between a JDK and an SDK
The JDK forms an extended subset of a software development kit (SDK). It includes "tools for developing, debugging, and monitoring Java applications".Oracle strongly suggests to now use the term JDK to refer to the Java SE Development Kit. The Java EE SDK is available with or without the JDK, by which they specifically mean the Java SE 7 JDK.
I need to know where JDK is located on my machine.
On running
Java -version in cmd, it shows the version as '1.8.xx'. To find the location of this SDK on my machine I tried using echo %JAVA_HOME% but it is only showing 'JAVA_HOME' (as there is no 'JAVA_PATH' var set in my environment variables).
If you are using Windows:
c:\> for %i in (java.exe) do @echo. %~$PATH:i This gives: C:\ProgramData\Oracle\Java\javapath\java.exe
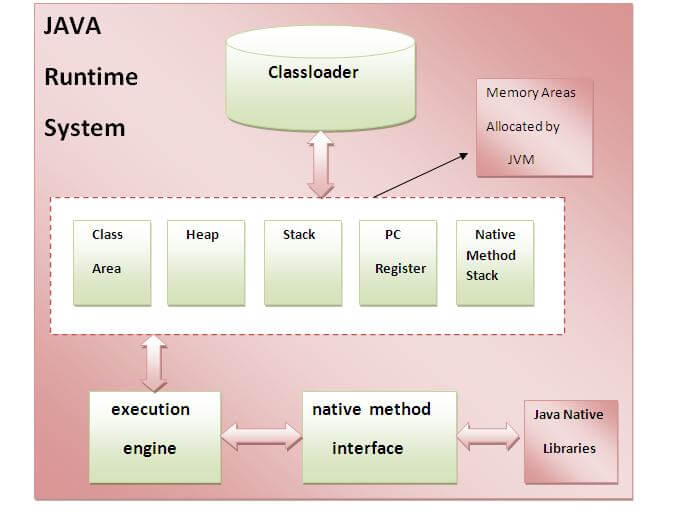
JVM provides definitions for the:
- Memory area
- Class file format
- Register set
- Garbage-collected heap
- Fatal error reporting etc.

1) Classloader
Classloader is a subsystem of JVM that is used to load class files.
2) Class(Method) Area
Class(Method) Area stores per-class structures such as the runtime constant pool,
field and method data, the code for methods.
field and method data, the code for methods.
3) Heap
It is the runtime data area in which objects are allocated.
4) Stack
| Java Stack stores frames.It holds local variables and partial results, and plays a part in method invocation and return. |
| Each thread has a private JVM stack, created at the same time as thread. |
| A new frame is created each time a method is invoked. A frame is destroyed when its method invocation completes. |
5) Program Counter Register
PC (program counter) register. It contains the address of the Java virtual machine instruction currently being executed.
6) Native Method Stack
It contains all the native methods used in the application.
7) Execution Engine
| It contains: | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 1) A virtual processor | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2) Interpreter: Read bytecode stream then execute the instructions. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 3) Just-In-Time(JIT) compiler: It is used to improve the performance.JIT compiles parts of the byte code that have similar functionality at the same time, and hence reduces the amount of time needed for compilation.Here the term ?compiler? refers to a translator from the instruction set of a Java virtual machine (JVM) to the instruction set of a specific CPU. What happens at compile time?At compile time, java file is compiled by Java Compiler (It does not interact with OS) and convertsthe java code into bytecode. 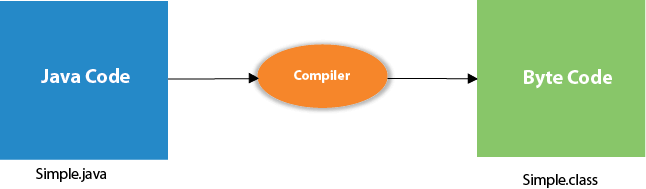 What happens at runtime?
|
Comments
Post a Comment